Electrification projects across states are transforming access to reliable power nationwide. These programs aim to connect every household and strengthen local economies.
Supported by government initiatives, private investments, and renewable technologies, progress continues to accelerate.
This article highlights major achievements, challenges, and innovations shaping electrification in different regions.
Understanding Electrification and Its Importance
Expanding access to electricity plays a vital role in driving social and economic progress.
Understanding the concept helps citizens recognize how essential electrification is to a country’s growth.
What Does Electrification Mean?
Electrification involves expanding grid networks, connecting remote regions, and adopting renewable power sources.
This process also embraces modern technologies such as smart meters and automation for real-time monitoring.
The ultimate goal is to make electricity accessible, affordable, and sustainable for all.
Economic and Social Benefits
Reliable electricity access strengthens national development and everyday life. It allows students to study after dark, clinics to store vaccines, and small businesses to grow.
Electrified communities also experience improved job creation and digital connectivity.
These social and economic benefits make electrification one of the most transformative development priorities.
National Goals for Electrification
The government’s vision includes:
- Achieving universal household connectivity
- Strengthening rural and urban grid reliability
- Integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind
- Reducing dependency on non-renewable fuels
Each objective aligns with India’s broader mission to become a sustainable energy leader by ensuring all citizens have dependable electricity.
Overview of Electrification Progress Across States
Each state has adopted different models to accelerate electrification. Some regions focus on grid expansion, while others invest heavily in renewable systems.
States Leading the Way
Several states have achieved near-universal power access. Gujarat and Maharashtra lead with efficient industrial electrification and stable distribution networks.
Tamil Nadu and Kerala stand out for integrating renewable power at scale. Karnataka and Telangana have expanded rural electrification through community-based microgrids.
States Catching Up
Significant progress has also been observed in Bihar, Odisha, Uttar Pradesh, and Assam. Rural-focused schemes have improved connectivity and reliability in these areas.
These states continue to bridge gaps in last-mile distribution through government and private collaboration.
Their experiences demonstrate that targeted funding can deliver measurable results.
Electrification in Remote Regions
Reaching remote and hilly regions remains a major challenge. States in the Northeast, along with Jammu & Kashmir and Andaman & Nicobar Islands, are deploying solar microgrids and hybrid systems.
These setups reduce transmission losses and improve local power independence. Such innovations highlight how decentralization supports full national coverage.
Key Electrification Schemes and Initiatives
Several major programs drive the electrification agenda across India. These initiatives combine federal funding, technological support, and local implementation.
Saubhagya (Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana)
Launched to ensure every home receives power, Saubhagya has connected millions of rural households. The scheme simplifies documentation and accelerates line installations.
It also includes awareness campaigns encouraging regular electricity usage and payments. The program has become a foundation for other energy-access projects.
Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY)
This scheme focuses on rural feeder separation and sub-transmission upgrades. It strengthens the power supply in agriculture and residential areas separately.
DDUGJY has also enabled the installation of decentralized generation units for remote zones. This decentralization ensures a steady supply even during main-grid disruptions.
Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS)
The RDSS enhances grid reliability through smart meters, predictive maintenance, and loss reduction. It emphasizes technology-based efficiency and data transparency.
This modernization reduces financial stress on utilities while improving service quality. States adopting RDSS report better operational performance and customer satisfaction.
State-Led Programs
Some states have launched their own programs to complement central schemes.
Examples include Delhi’s smart grid pilot, Maharashtra’s industrial upgrades, and Kerala’s renewable distribution hubs.
These initiatives adapt national goals to local realities. Local innovation ensures faster, region-specific outcomes.
Funding and Investment in Electrification Projects
Electrification success relies on adequate financial resources. Funding comes from a mix of public budgets, private partnerships, and global support.
Understanding these streams highlights how large-scale energy projects are sustained.
Central and State Funding Contributions
The central government provides grants for infrastructure and distribution expansion. States manage localized initiatives that complement national programs.
Together, they coordinate to ensure equitable resource allocation. Consistent monitoring prevents overlapping and improves efficiency.
Private Sector Participation
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) play a growing role in electrification. Corporate investments in smart grids and renewable systems drive innovation and speed.
These collaborations improve access in underserved areas and foster economic activity. They also create new employment opportunities in the clean energy sector.
International Support and Green Financing
Foreign aid and sustainable finance mechanisms strengthen energy projects further. World Bank and Asian Development Bank (ADB) loans back renewable infrastructure upgrades.
Green bonds and climate funds promote environmentally responsible investment. These global partnerships align India’s goals with international climate commitments.
Focus on Renewable Energy Integration
The push for renewable energy integration defines the next phase of electrification. States are replacing fossil-based systems with cleaner, smarter technologies.
This shift ensures energy security while reducing carbon emissions. The growing synergy between electrification and sustainability promises long-term resilience.
Solar Power Projects
Solar power plays a key role in decentralized electrification. Major projects like Rewa Solar Park in Madhya Pradesh and Kamuthi Solar Plant in Tamil Nadu lead capacity expansion.
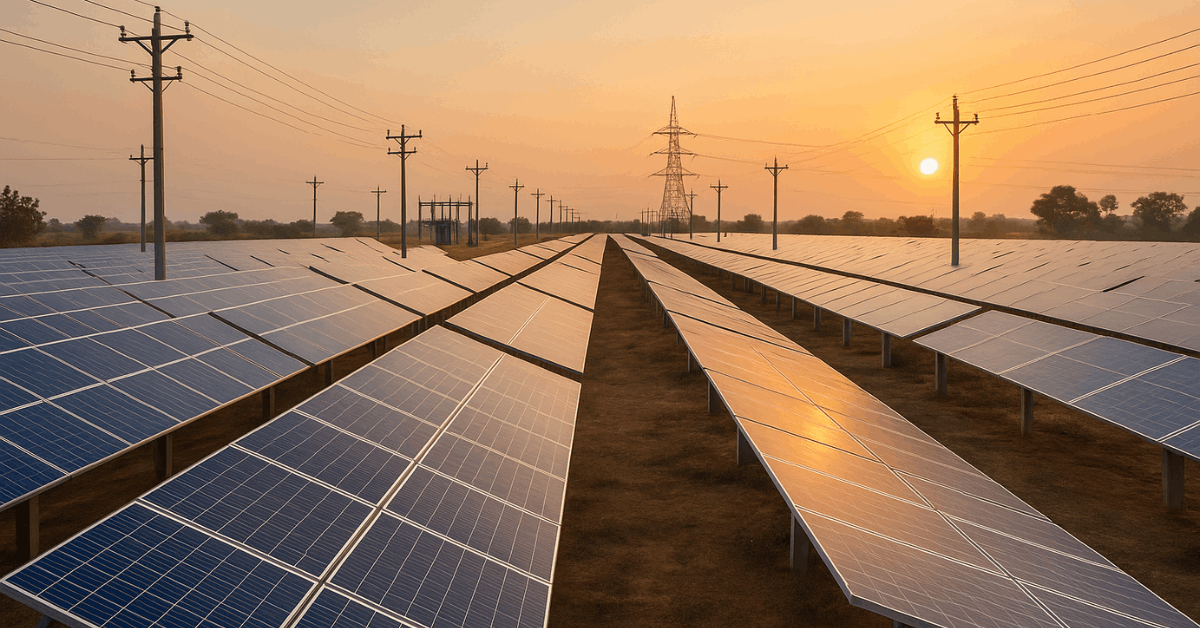
States also promote rooftop solar programs for homes and small businesses. These efforts enhance grid flexibility and cut dependence on traditional power plants.
Wind and Hydro Expansion
Wind farms in Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, and Rajasthan contribute significantly to renewable capacity.
Similarly, hydropower projects in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand support consistent supply during demand peaks.
Combining multiple renewable sources stabilizes grids across diverse climates. This integration supports India’s commitment to sustainable growth.
State Incentives for Green Power
Many states offer incentives to promote renewable adoption. Common examples include subsidies for rooftop installations, tax benefits, and feed-in tariffs.
Governments also support net metering policies to encourage household participation.
These incentives make clean energy economically attractive for consumers and investors.
Challenges in Electrification Implementation
Despite major progress, achieving complete electrification remains complex. Certain logistical, financial, and environmental barriers persist.
Infrastructure Gaps
Aging infrastructure limits grid efficiency in several regions. Transmission losses, poor maintenance, and unstable supply affect rural reliability.
Upgrading old systems with smart grids reduces these weaknesses. Continuous investment is needed to maintain power quality and consistency.
Financial and Administrative Constraints
Funding delays and policy bottlenecks slow down project execution. Some states face shortages of trained technical personnel for maintenance.
Administrative coordination across departments also affects timelines. Streamlined management could speed up project delivery significantly.
Natural and Geographical Barriers
Remote and challenging terrain poses serious difficulties in connecting grids. Floods, landslides, and seasonal monsoons often disrupt installations.
In such areas, off-grid and microgrid systems provide more reliable solutions. Flexible project designs help ensure uninterrupted service despite environmental constraints.
Technology and Innovation in Electrification
Modern technology plays a defining role in improving power distribution. Automation, digital tracking, and data analysis strengthen the system from generation to delivery.
States adopting innovative solutions achieve higher efficiency and transparency. These technologies also reduce long-term operational costs.
Smart Grids and Meters
Smart grids enable real-time monitoring, energy load balancing, and automatic fault detection. They enhance distribution efficiency and reduce downtime.
Smart meters allow customers to track consumption, improving billing accuracy. Together, they create an intelligent energy network that supports sustainability.
Data Analytics and Forecasting
Using big data analytics, utilities can forecast demand and prevent power shortages. Predictive tools optimize energy flow and identify high-loss areas.
This insight improves both performance and planning accuracy. The result is a smarter, more responsive energy infrastructure.
Emerging Trends
These emerging trends will continue to transform electrification in the coming decade.
- AI-driven energy forecasting improves demand prediction accuracy.
- Battery storage technology ensures steady power during fluctuations.
- Decentralized renewable microgrids support independent community power systems.
Final Thoughts: Powering the Nation’s Future
The nationwide push for electrification projects has reshaped how energy is produced and distributed.
States are combining smart technology, renewable energy, and innovative financing to reach every household.
With consistent commitment, collaboration, and investment, full electrification across all states is no longer a distant goal—it’s becoming a national reality.











